1. Introduction
Choosing the right Push button switches might seem straightforward, but there’s a lot more to it than meets the eye. Whether you’re working on an industrial machine, a piece of consumer electronics, or a home automation system, the right switch can make all the difference. Let’s dive into everything you need to know to make an informed decision.

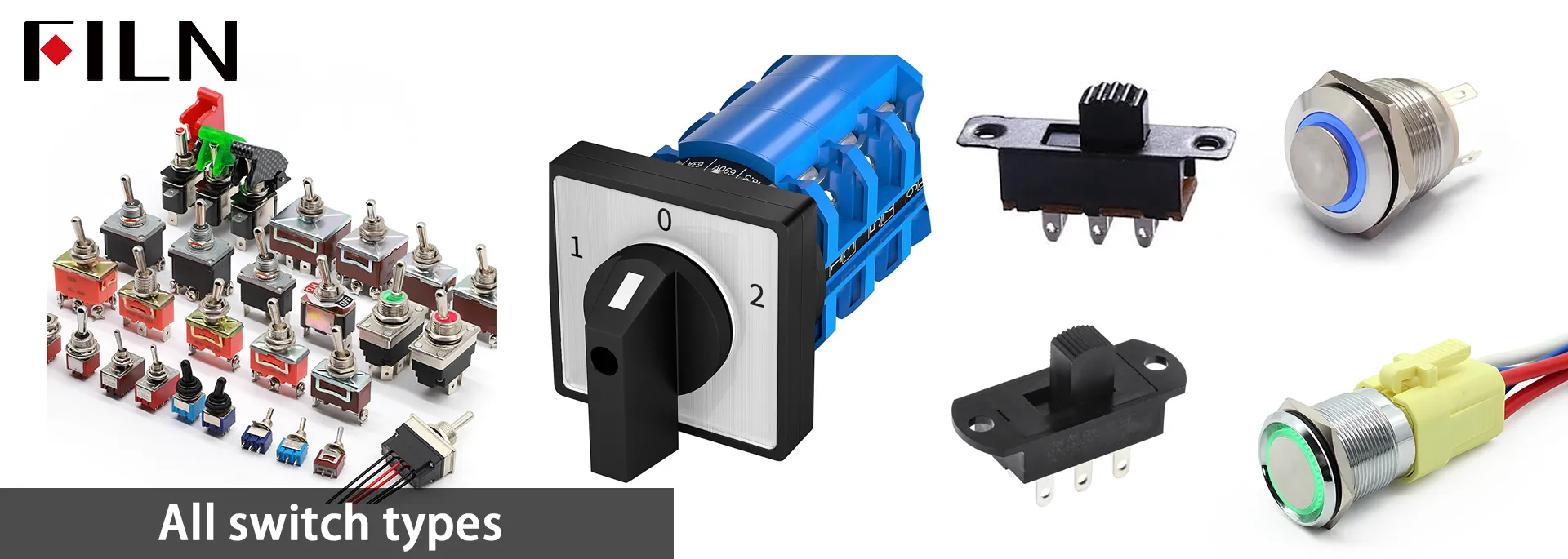
2. Types of Push Button Switches
- Emergency stop button switch:
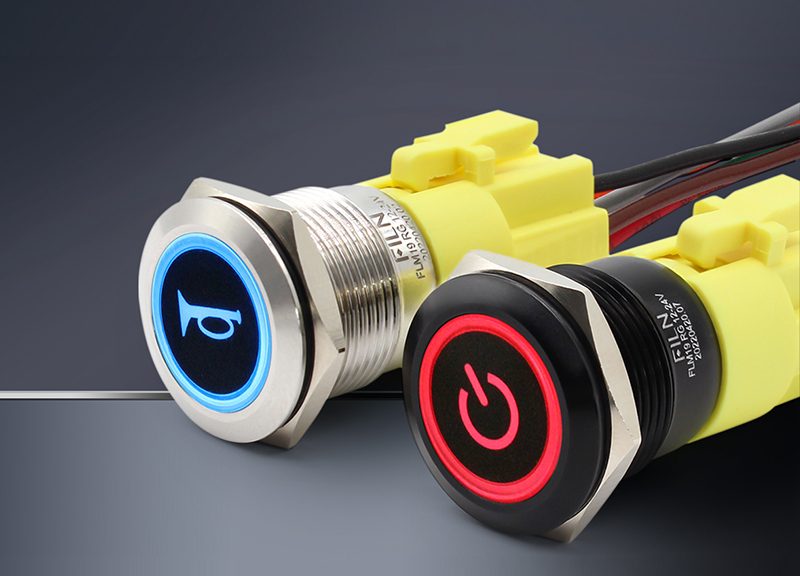
as the name suggests is the emergency stop button switch, some large industrial equipment need to be equipped with an emergency stop button switch in order to prevent the occurrence of danger, FILN developed a waterproof IP67 emergency button switch, which is relatively rare on the market. FILN also offers lighted emergency stop switches. - Ultra-thin tactile button switches:
These types of button switches are much smaller in size compared to conventional ones, primarily designed for use in confined spaces. They feature a short-stroke tactile mechanism, which provides a better feel and operational experience.
FILN has developed various wiring methods to cater to different installation environments, including pin switches that directly connect to the circuit board, connector button switches that can be plugged and unplugged with connectors, and wire-attached ultra-thin button switches with a certain level of waterproof capability.

3. How Push Button Switches Work
The mechanics behind the functioning of push button switches are fairly straightforward.
When the button is pressed, it forces a conductive element—typically metallic—to bridge the gap between the two contacts, thereby forming a complete electrical circuit. This action facilitates the flow of current through the switch, powering the device it’s connected to.
However, when the button is released, the contacts are disconnected, resulting in the circuit being broken and the flow of current being ceased.
3. Applications of Push Button Switches
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, push button switches are used to control machinery and equipment. They need to be robust, durable, and reliable to withstand harsh environments.
Consumer Electronics
From power buttons on your TV remote to game controllers, push button switches are integral to consumer electronics. They need to be responsive and durable.
Automotive Applications
Cars use push button switches for various functions, such as starting the engine or controlling the stereo. These switches must be able to endure vibrations and extreme temperatures.
Home Automation
In smart homes, push button switches control lighting, security systems, and other automated features. They should be easy to use and aesthetically pleasing.

4. Key Factors to Consider

5. Understanding Electrical Ratings
6. Mechanical Durability
7. Aesthetic and Ergonomic Considerations
- Design and Finish
The switch’s appearance should match your application’s design. Consider color, texture, and overall look. - Size and Shape
Make sure the switch is the right size and shape for its intended use. It should fit comfortably where it will be installed. - User Experience
A switch should be intuitive and easy to use. Test it to ensure it provides a good user experience.
10. Choosing the Right Manufacturer
- Reputation and Reviews
Research manufacturers and read reviews to find a reputable supplier. A good manufacturer will provide reliable, high-quality switches. - Warranty and Support
Check for warranties and customer support options. This can be crucial if you encounter issues with your switch. - Customization Options
Some manufacturers offer customization options. If you need a specific design or feature, look for manufacturers who can accommodate your needs.
FILN is a professional manufacturer of pushbutton switches, we can customize the appearance of the buttons described above, the size of the dimensions and any knowledge related to pushbutton switches.
Currently, we have 10 push button switch technical engineers, we are confident that we can solve any switch problem quickly, serve every customer one to one, and keep developing new push button switches to pay our part for this society.

11.Choosing the Right Push Button Switch
Selecting the right push button switch for your application involves several factors:
- Load Requirements: Ensure the switch can handle the electrical load of your application.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider factors such as moisture, temperature, and dust that the switch will be exposed to.
- Application-Specific Needs: Choose a switch that meets the specific requirements of your application, such as illumination, size, and mounting style.
Conclusion
Choosing the right push button switch involves considering various factors, from electrical ratings to environmental conditions and user experience. By understanding your specific needs and researching your options, you can find the perfect switch for your application.
Choosing Push Button Switch FAQs
1. What is the difference between a momentary and a latching push button switch?
A momentary switch is only active while pressed, while a latching switch stays in one state until pressed again.
2. How do I determine the right electrical rating for my application?
Check the voltage and current requirements of your application and choose a switch with matching or higher ratings.
3. Can push button switches be used outdoors?
Yes, but ensure they have a suitable IP rating for protection against dust and water.
4. What should I consider when choosing the design of a push button switch?
Consider the aesthetic, ergonomic factors, and how well the design fits your application.
5. How do I maintain and clean my push button switch?
Regularly inspect and clean the switch, following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Replace any worn-out parts to maintain performance.